What to Know About Aerospace Cleanroom Filtration
Your cleanroom filtration system is arguably the most important part of any aerospace cleanroom. Air purity is the foundation of your cleanroom classification standard, with equipment and materials of the cleanroom designed around maintaining a strict quality standard. Let’s dive into cleanroom filtration in aerospace cleanrooms, how it works, and how it relates to the cleanroom classification.
How Aerospace Cleanroom Filtration Works
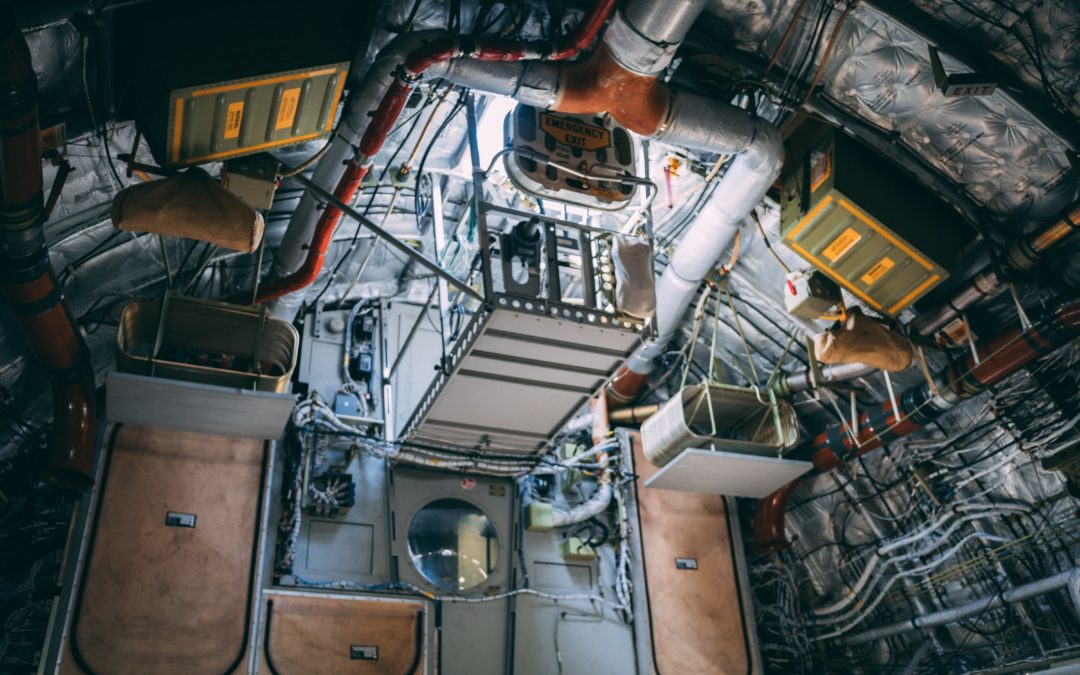
Before clean air can enter the cleanroom, it must first be heated, cooled, and have the humidity regulated by the cleanroom HVAC system. Then the treated air passes through various filters to remove particles up to a certain number and size, as prescribed by your aerospace cleanroom classification. There are four ways particles are collected using cleanroom filtration:
- Straining: Particles that are small enough pass through the fibers of the filter. Larger particles are prevented from entering the cleanroom.
- Impaction: Particles are pushed at the filters and become stuck to the fibers through impaction.
- Interception: Filter creates a block against large particles, but small particles may seep around the filter in small airstreams.
- Diffusion: Air molecules in motion cause smaller particles to vibrate, which gives them more opportunities to be collected by the filter’s fibers. Smaller particles are more likely to vibrate than larger ones.
An aerospace cleanroom filtration system likely uses multiple filters to achieve properly filtered air. Depending on the stringency of the classification, more filters may need to be used to reach the upper levels of purity standards.
Aerospace Cleanroom Filtration Components
Multi-stage HEPA filtration systems or a combination of HEPA and ULPA filters collect particles, allowing aerospace cleanrooms to effectively and efficiently maintain air quality, while actively removing hydrocarbons, silicones, and microbiological contaminants.
The HEPA filters are protected by prefilters, which remove large particles before air reaches the more expensive filters. They are vital for any cleanroom filtration system to protect and extend the life of HEPA filters. Because they are the most exposed, they must be replaced more often — usually around 6 times per year, depending on the application and operation level of the cleanroom.
The cleanroom filtration system is packaged in modules called filter/fan units. These units are typically installed in the ceiling grid of the cleanroom where they fit seamlessly into the cleanroom design, leaving no room for contaminating particles to settle.
Cleanroom Filtration Requirements for Aerospace Cleanrooms
Most aerospace cleanrooms must comply with ISO 14644-1 Class 7 or ISO Class 8 requirements for air quality and filtration. However, more extreme standards may apply for highly sensitive applications, requiring airborne particle concentrations to be strictly controlled to prevent disruption of processes within the cleanroom. For example, the development of spacecraft hardware, fine electronics, optical devices, or electronic sensory components will likely be regulated within a cleanroom that is ISO Class 7 or lower.
The ISO Class 7 standard sets the maximum level of particles 0.5 µm or larger at 352,000. To reach this, the cleanroom must have a ceiling coverage dedicated filtration of 15-20% and an average air change rate of approximately 60-90 complete changes per hour.
An aerospace cleanroom filtration system works hard to meet these requirements to maintain strict air quality standards, and must be supported by other systems in the cleanroom to be successful, such as the cleanroom HVAC and cleanroom design.
Maintaining Aerospace Cleanroom Filtration
Once you’ve achieved the proper level of cleanroom filtration in your aerospace cleanroom, you’ll need to closely monitor it to ensure the air quality is consistent. The best way to do this is to schedule regular inspections and perform routine maintenance on your cleanroom filtration system.
With regard to the cleanroom filtration system, all filters should be periodically checked and replaced when they are no longer working efficiently. For pre filters, this amounts to many times per year, while other filters, including HEPA filters, may not need to be replaced as often. Depending on the application and classification for each cleanroom, HEPA filters have a lifespan between 3 and 10 years.
A cleanroom with ineffective filters isn’t a cleanroom at all. If you’re installing a filtration system or upgrading your cleanroom’s filters, Angstrom Technology can help! Our cleanroom design experts can make sure your air flow pattern is working effectively and set you up with the right filters for your application. We can also add you to our maintenance and cleaning schedule so you don’t have to worry when it’s time to replace your filters. Get in touch with Angstrom Technology to learn more.